Heliosphere – where the solar wind meets the interstellar medium

Credit: NASA’s GSFC Conceptual Image Lab
The outer space between stars, planets, and other celestial bodies is often referred to as an example of an almost perfect vacuum. While it is a much better vacuum than achievable in laboratories, the rarefied matter in and around the Solar System plays an important role in the development of life on Earth.
The main source of interplanetary medium is the Sun, which continuously blows out a hot plasma from the solar corona with speeds of ~300-800 km/s called the solar wind. As the solar wind expands, the density drops, and eventually, the pressure of the interstellar medium prevents further expansion, enclosing the solar wind within the heliosphere.
The heliosphere expands more than 100 au from the Sun. The solar wind and interstellar plasmas are magnetized, and the electromagnetic forces prevent the direct penetration of interstellar charged particles into the heliosphere. Therefore, the heliosphere shields Earth from the direct impact of most galactic cosmic rays.
In my research, I study the shape and processes in the heliosphere and the neighboring interstellar medium. I use observations of neutral atoms, which travel between collisions on scales exceeding the heliosphere’s size. Consequently, they can be used as messengers from distant regions of the heliosphere and interstellar medium.
Interstellar neutral (ISN) atoms

Interstellar neutral (ISN) atoms originate from the very local interstellar medium around the heliosphere and can be observed with a detector placed on spacecraft close to Earth. In my research, I use observations of ISN helium atoms from the IBEX mission. Because many of these atoms are only affected by the Sun’s gravity, we use them to study the physical conditions in the interstellar medium.
Select publications:
- Swaczyna, P., Bzowski, M., Heerikhuisen, J., et al., 2023, Interstellar Conditions Deduced from Interstellar Neutral Helium Observed by IBEX and Global Heliosphere Modeling, The Astrophysical Journal, 953, 107, [DOI, ADS].
- Swaczyna, P., Schwadron, N. A., Möbius, E., et al., 2022, Mixing Interstellar Clouds Surrounding the Sun, The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 937, L32, [DOI, ADS].
- Swaczyna, P., Kubiak, M. A., Bzowski, M., et al., 2022, Very Local Interstellar Medium Revealed by a Complete Solar Cycle of Interstellar Neutral Helium Observations with IBEX, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 259, 42, [DOI, ADS].
- Swaczyna, P., Bzowski, M., Kubiak, M., et al., 2015, Interstellar Neutral Helium in the Heliosphere from IBEX Observations. I. Uncertainties and Backgrounds in the Data and Parameter Determination Method, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 220, 26, [DOI, ADS].
Pickup ions (PUIs)
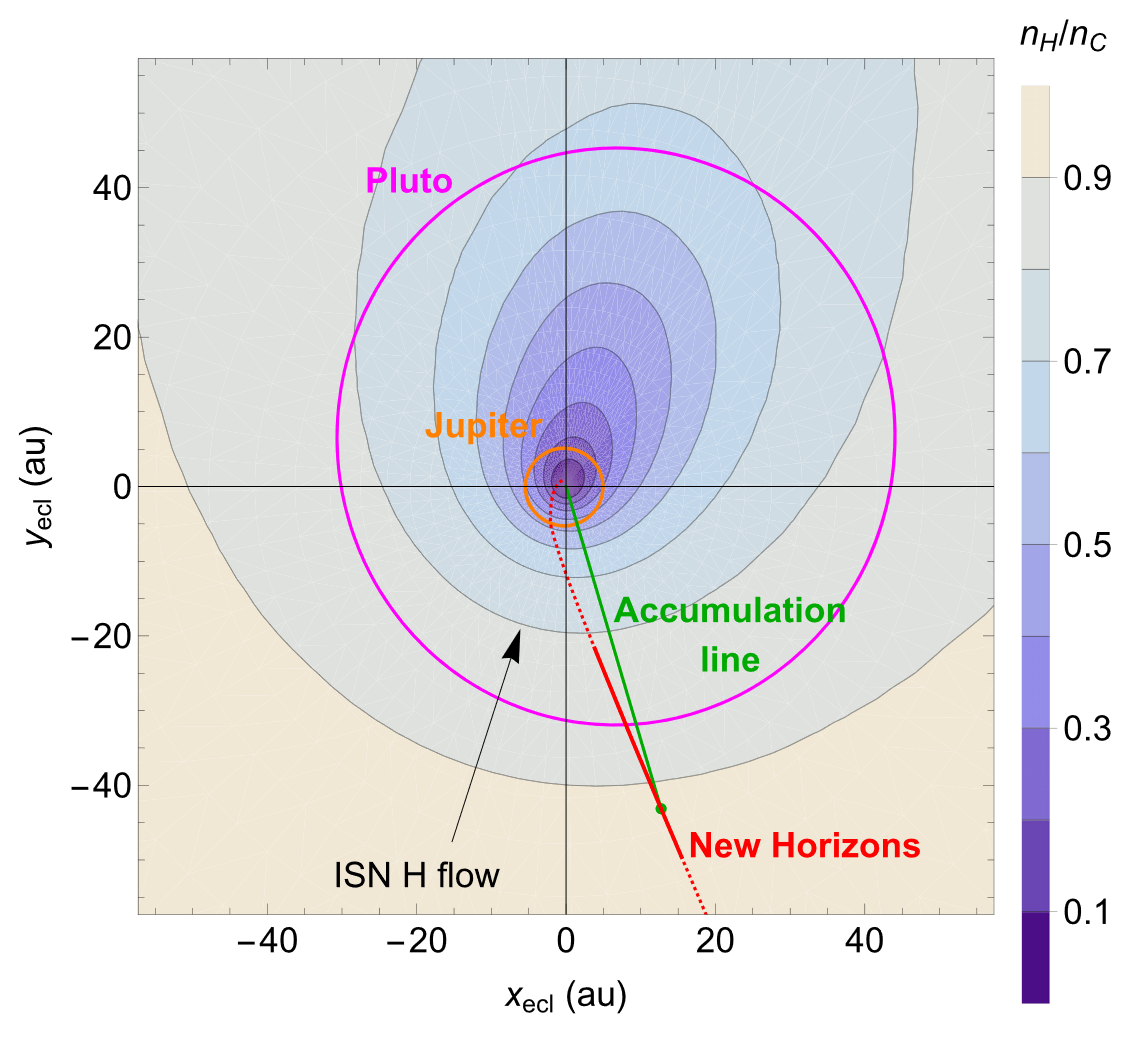
Credit: Swaczyna et al. (2024, ApJL 969:L20, Fig. 1)
ISN atoms ionized in the solar wind are picked up by the solar wind plasma are called pickup ions. These ions are significantly more energetic in the solar wind frame because their initial (pickup) speed is given by the relative velocity of the ISN atoms and plasma, which in the supersonic solar wind is ~400-800 km s-1. Within a few au from the Sun, the PUIs dominate the solar wind internal pressure. Consequently, they play a key role in the dynamic of the heliosphere. In distant solar wind, the PUIs are detected by the New Horizons mission. We expect that PUIs are preferentially heated at the heliospheric termination shock and are source of energetic neutral atoms.
Select publications:
- Swaczyna, P., Bzowski, M., Dialynas, K., Dyke, L., Fraternale, F., Galli, A., Heerikhuisen, J., Kornbleuth, M. Z., Koutroumpa, D., Kowalska-Leszczyńska, I., Kubiak, M. A., Michael, A. T., Müller, H.-R., Opher, M., & Rahmanifard, F., 2024, Interstellar Neutral Hydrogen in the Heliosphere: New Horizons Observations in the Context of Models, The Astrophysical Journal Letters, 969, L20, [DOI, ADS].
Swaczyna, P., McComas, D. J., Zirnstein, E. J., Sokół, J. M., Elliott, H. A., Bzowski, M., Kubiak, M. A., Richardson, J. D., Kowalska-Leszczynska, I., Stern, S. A., Weaver, H. A., Olkin, C. B., Singer, K. N., & Spencer, J. R., 2020, Density of Neutral Hydrogen in the Sun’s Interstellar Neighborhood, The Astrophysical Journal, 903, 48, [DOI, ADS].
- Swaczyna, P., McComas, D. J., & Zirnstein, E. J., 2019, He+ Ions Comoving with the Solar Wind in the Outer Heliosphere, The Astrophysical Journal, 875, 36, [DOI, ADS].
Energetic neutral atoms (ENAs)
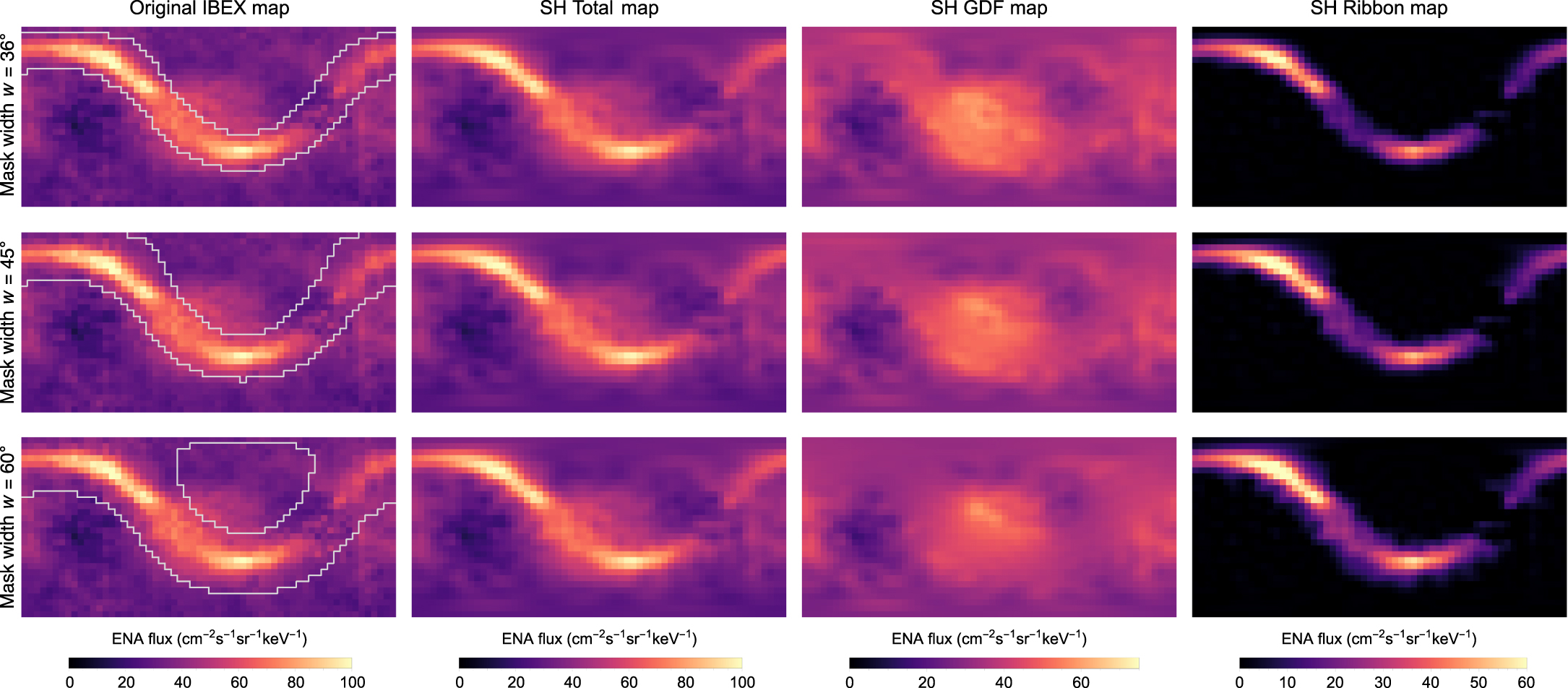
Credit: Swaczyna et al. (2023, ApJS 266:26, Fig. 4)
Imaging the heliosphere using observations of ENA fluxes at 1 au on the IBEX mission allows tracking the heliosphere’s solar-cycle evolution. The ENA flux maps show two sources having different geometric properties at the energies the IBEX instruments cover. The globally distributed flux extends over the sky and originates mostly from the inner heliosheath. The other source forms a narrow, almost circular structure called the IBEX ribbon. This feature was not expected before the IBEX mission launch. In my research, I develop methods to separate these two sources’ signals to enable individual interpretation of these observations. I also study the geometric properties of the ribbon to uncover its origin.
Select publications:
- Swaczyna, P., Dayeh, M. A., & Zirnstein, E. J., 2023, Spherical Harmonic Representation of Energetic Neutral Atom Flux Components Observed by IBEX, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 266, 26, [DOI, ADS].
- Swaczyna, P., Eddy, T. J., Zirnstein, E. J., et al., 2022, IBEX Ribbon Separation Using Spherical Harmonic Decomposition of the Globally Distributed Flux, The Astrophysical Journal Supplement Series, 258, 6, [DOI, ADS].
- Swaczyna, P., Bzowski, M., & Sokół, J. M., 2016, The Energy-Dependent Position of the IBEX Ribbon Due to the Solar Wind Structure, The Astrophysical Journal, 827, 71, [DOI, ADS]. (Erratum: Swaczyna, P., Bzowski, M., & Sokół, J. M., 2018, The Astrophysical Journal, 854, 186, [DOI, ADS].)
- Swaczyna, P., Bzowski, M., Christian, et al., 2016, Distance to the IBEX Ribbon Source Inferred from Parallax, The Astrophysical Journal, 823, 119, [DOI, ADS].
